OpenBCI 101
Our lab uses OpenBCI peripherals. In order to measure EEG signal from an individual, you need two things. (1) Sensors (2) Sensor Reader
- Sensors: are the electrodes that sense the voltage at a given time. There sensors are attached to the hat.
- Sensor Reader: is an electronic board connected to a hat and collect data. The board will also be controlled from a host (usually a computer).
Peripheral Setup
A brief setup is shown below in a pdf format.
For more detail, watch YouTube video
OpenBCI - Python developer
For developer, right now OpenBCI suggest we to use BrainFlow library. Link
For using exiting project, you will likely be using pyOpenBCI, pylsl, and bluepy. Link
The package you need are
pip install numpy pyserial bitstring xmltodict requests bluepy pyOpenBCI pylsl==1.12.2
To complete the installation, read the Troubleshooting
EEG offset/ DC offset/ Drift/ slow cortical potentials (SCP)
TLDR; Use a High-Pass filter at 1Hz to remove this DC offset. What if your interested EEG frequency range is in that 0-1 Hz? Well, good luck.
- DC-EEG in Psychophysiology Applications – A Technical and Clinical Overview -> https://www.bmedreport.com/archives/3739
- Huge offset. Possible causes? -> https://openbci.com/forum/index.php?p=/discussion/2595/huge-offset-possible-causes
- large millivolt data values / FbEEG (Full-Band EEG) -> https://openbci.com/forum/index.php?p=/discussion/201/large-millivolt-data-values-fbeeg-full-band-eeg
Troubleshooting
Problem 1: Cannot access /dev/ttyUSB0 without sudo
Solution: Add user to dialout group. (Choose 1 command below)
# For create a new user and assign to `dialout` group
$ sudo adduser <username> dialout
# For assigning existing user to `dialout` group
$ sudo usermod -a -G dialout <username>
Problem 2: EEG not found - when run lsl-viewer.py
Solution: Downgrade pylsl
$ pip3 uninstall pylsl
$ pip3 install -I pylsl==1.12.2
Problem 3: Segmentation fault Core Dump - when run lsl-viewer.py
Solution: Change matplotlib backend
$ pip3 install pyqt5
$ sudo apt-get install python3-pyqt5
$ sudo apt-get install pyqt5-dev-tools
$ sudo apt-get install qttools5-dev-tools
$ sudo apt-get install libglib2.0-dev python3-dev
Below is the script for benchmarking your matplotlib
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/5091993/list-of-all-available-matplotlib-backends
from __future__ import print_function, division, absolute_import
from pylab import *
import time
import matplotlib.backends
import matplotlib.pyplot as p
import os.path
def is_backend_module(fname):
"""Identifies if a filename is a matplotlib backend module"""return fname.startswith('backend_') and fname.endswith('.py')
def backend_fname_formatter(fname):
"""Removes the extension of the given filename, then takes away the leading 'backend_'."""return os.path.splitext(fname)[0][8:]
# get the directory where the backends live
backends_dir = os.path.dirname(matplotlib.backends.__file__)
# filter all files in that directory to identify all files which provide a backend
backend_fnames = filter(is_backend_module, os.listdir(backends_dir))
backends = [backend_fname_formatter(fname) for fname in backend_fnames]
print("supported backends: \t" + str(backends))
# validate backends
backends_valid = []
for b in backends:
try:
p.switch_backend(b)
backends_valid += [b]
except:
continueprint("valid backends: \t" + str(backends_valid))
# try backends performancefor b in backends_valid:
ion()
try:
p.switch_backend(b)
clf()
tstart = time.time() # for profiling
x = arange(0,2*pi,0.01) # x-array
line, = plot(x,sin(x))
for i in arange(1,200):
line.set_ydata(sin(x+i/10.0)) # update the data
draw() # redraw the canvasprint(b + ' FPS: \t' , 200/(time.time()-tstart))
ioff()
except:
print(b + " error :(")
Problem 4: If you see a similar message in the picture when trying to run “lsl-stream.py”, the issue might be no internet connection.
Solution: Connect to the internet
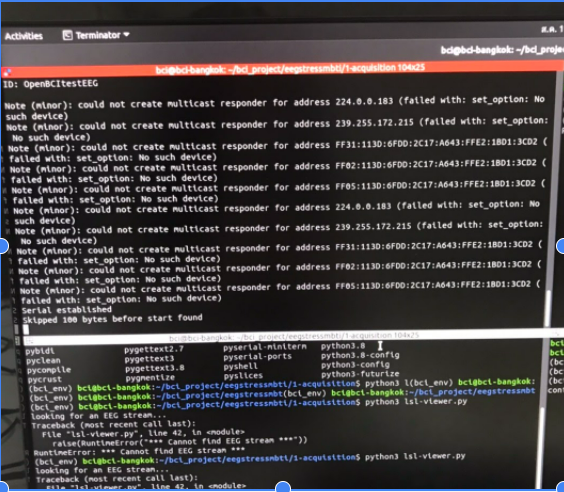
https://mailman.ucsd.edu/pipermail/lsl-l/2017/000306.html https://github.com/sccn/liblsl/commit/4df71008570e2f4b01e3a19ee79aa529514d8d3d I know it is odd that the library requires an internet connection, but it is. (T _ T)